(www.c10mt.com) If it was a few years ago that payment cards, especially credit cards, was still an unfamiliar concept to many people, buying on it now is a quite normal phenomenon in the lives of many people nowadays. According to statistics from Nilson (2013), the rate of using payments cards worldwide by brand continues to increase until 2017, especially UnionPay cards. Although just over 10 years, UnionPay has risen to become most brand chosen since its inception in 2002, overcome serious competitor – Visa. According to the chart, the highest proportion are UnionPay cards, MasterCard cards and Visa cards with the total cards amount issued worldwide respectively 3.5 million, 2.5 million and 1.2 million.
 |
| Credit Card and HCMC Young People Research Methodolory |
Title | Credit Card and HCMC Young People
We can say that with credit cards, people are no longer have to carry cash when they want to go shopping, or travel abroad so “handy”, “compact” and “efficient” are basically what people used credit card can describes about. And moreover, the factors that affect the intended decision to use credit card of people are important too because lots of people own cards but rarely use them in daily life.
 |
| Total Payment Cards and Growth in Global Brands worldwide – 2012 vs. 2017 (The Nilson Report, 2013) |
Since the youth (fewer than 40 year olds) are the “high potential” of the range of above expected income, they form an attractive potential market for credit card companies. Our group will focus on discovering the factors mainly affect the customers’ spending by credit cards. This dissertation is about the introduction and whole background of the topic we decided on. This is also followed by the problem statement and research questions, which form the basis of this thesis.
Background | Credit Card and HCMC Young People
According to the statistic, the credit growth of banking sector in 2012-2013 was recorded by 8.91%. The proportion of consumer lending portfolios increase from 53% to 57% on total asset which corporation lending occupies nearly 50% of total credit of 33 commercial banks ( consumer lending nearly 30%) (KPMG Audit Company 2013).
On the one hand, the fact that Vietnam acceding WTO in 2008 helps create many opportunities to have a lot of different liquidate method in which using credit card, visa card are attractive more from personal consumer. According to the Vietnam State Bank, to the end of 2010 there are 49 organizations issuing over 200 types of cards. It was about nearly 24 million cards issued. Till now (02/2014), there are 52 companies have registered for issuing cards, with more than 64 million issued cards, around 14,700 ATMs and 122,000 POS set up nationwide.
Classifying in term of range, a report of State bank of Vietnam showed that there were 6.34 million international cards has issued at the end of 2013, increased 57.3%, which accounts nearly 10% of total cards. In term of financial sources, total number of credit cards grew up by 50% to 2.43 million cards, while the number of debit cards was 2.67 million cards when compared with 2012.
Credit cards gradually become a potential market for banks to exploit because there are too many cards were issued that leads to the saturation of the market. However, there are so many aspects that they should be consider if they want to extend this market such as the using cash behavior of Vietnamese people, their education, or their personal culture… According Vietnam Card Association numbers, at the end of 2011, the total transaction by card in Vietnam increasing to 32 billion dollar. However, the using cash behavior still occupied a large of proportion (nearly 80%) . Represented by Co.opmart, Big C, Citimart, Maximark said that the transaction without cash proportion just occupied nearly 1% and do not over 5% on total revenue.
According to the not yet official statistics, Ho Chi Minh City has around 20 million cards , which means each people has about 2 to 3 cards. Consequently, people own credit cards but not spending as much as that of cash (cash is still occupied nearly 97% of spending behavior) . Which means that people are already ready with cards but why they are still hesitate to use those, what factors are influencing them? This analysis research will investigate based on the qualitative method with main object is the youth in Ho Chi Minh City will be help us to understand more about the external aspect to impact on using credit card behavior in Ho Chi Minh City.
- Research Question
Major factors that affect the intended decision to use credit card of people in Ho Chi Minh City.
- Research Objective
First of all, we want to provide a descriptive study about the situation of using credit card worldwide and in Vietnam recent years. This will contain the numbers, the growth and the recent trends.
Secondly, we will figure out factors that affect the decision whether to use credit card as the mean of payment. The target customer will be people from 18 to 40 years old. Some of the potential factors can be listed such as income, satisfaction about promotion, the customer services quality and so on. We are tend to build the theoretical framework by measuring those factors to point out significant ones. During the research, there will be the collection, processing and analyzing relevant data.
After converting all the qualitative data into quantitative form, we will be able to use regression technique to determine significant factors, which is said to have significant effect to the usage of credit card. Our research is not only logical and theoretical but also practical.
Attaining the final result, this research can help banks to understand more about their customer's experience and their thoughts, expectation and tendency toward credit cards. That is exactly our desired achievement doing this research.
The Theory of Planned Behavior
The category of Customer Behavior studies how individuals, groups, organizations select and use goods, services and ideas to satisfy their needs (X. Hung, 2013). In this proposal, we will only focus on individual consumer’s field, under age 40, living and working in Ho Chi Minh City.
Each consumer has influence and divergent thinking in consumer decision using products. The decision is effect by many different factors and this decisions also affect the survival and development of every business. Therefore, the research and learn about the intended leads to real behavior (or real action) of the customer will help businesses get the advantage over the stiff competition in today's society.
Introduce the Theory of Planned Behavior
In the second half of the 20th century, the advent of the Theory of reasoned Action - TRA (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) and the Theory of planned behavior - TPB (Ajzen, 1988, 1991) has subsequently recognized as a useful tool in predicting the user's attitude.
By aggregating different behaviors, observed on different occasions and in different situations, these other sources of influence tend to cancel each other, with the result that the aggregate represents a more valid measure of the underlying behavioral disposition than any single behavior. Many studies performed in recent years have demonstrated the workings of the aggregation principle by showing that general attitudes and personality traits do in fact predict behavioral aggregates much better than they predict specific behaviors (Ajzen, 1988, for a discussion of the aggregation principle and for a review of empirical research).
TRA is considered a pioneering model in the view of psychosocial factors in order to determine the trend-conscious behavior (Sheppard, Hartwick & Warshaw, 1988). However, TRA also had limited. TPB is an extension of TRA (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1980; Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) made necessary by the original model’s limitations in dealing with behaviors over which people have incomplete volitional control.
As in the original theory of reasoned action, a central factor in the Theory of Planned Behavior is the individual’s intention to perform a given behavior. Intentions are assumed to capture the motivational factors that influence a behavior; they are indications of how hard people are willing to try, of how much of an effort they are planning to exert, in order to perform the behavior. As a general rule, the stronger the intention to engage in a behavior, the more likely should be its performance. It should be clear, however, that a behavioral intention can lined expression in behavior only if the behavior in question is under volitional control, i.e., if the person can decide at will to perform or not perform the behavior.
According to Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1988, 1991), the model is depicted in Figure 5.1 and represents the three variables, which influence one another, will predict the intention to perform a behavior. Intentions are the precursors of behavior. Besides that, perceived behavioral control, together with behavioral intention, can be used directly to predict behavioral achievement.
To predict whether a person intends to do something, we need to know:
• Attitude Behavior - Whether the person is in favour of doing it
• Subjective Norm - How much the person feels social pressure to do it
• Perceived Behavior Control - Whether the person feels in control of the action in question
By changing these three ‘predictors’, we can increase the chance that the person will intend to do a desired action and thus increase the chance of the person actually doing it. In a clinical consultation, the clinician’s treatment decisions and actions are examples of intentional behavior.
Applied of the Theory of Planned Behavior.
From a general view, using the TPB to study consumer behavior is widely applied in many fields worldwide. For example, C. Kasem & N. Takashi (2010) has applied TPB to study the psychological factors affecting the intention to use overhead electric vehicles in Phnom Phenh, Cambodia; J. Francis, P. Eccles, A. Walker & R. Foy (2004) can investigate the attitudes and beliefs underlying health-related behavior by using TPB; Leann G. Rutherford & Sharon A. DeVaney (2009) completed their research about Utilizing the Theory of Planned Behavior to Understand Convenience Use of Credit Cards.
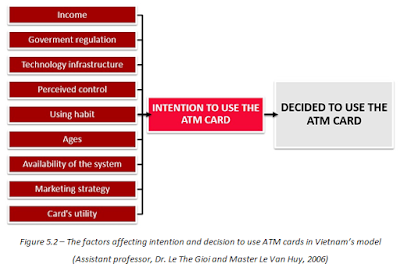
In Vietnam, this model has been successfully applied by Assistant professor, Dr. Le The Gioi and Master Le Van Huy in the study of factors affecting the intentions and decision to use ATM cards. Figure 5.2 will show their recommend model.
The theory of planned behavior is an appropriate theory for studying credit card usage behavior of consumers. The theory can be used to evaluate consumers’ general attitudes about credit, their feelings about the social norm pressure, and the difficulty of achieving the desired behavior. Previous research supports the factors used in the theory as predictors of credit card users (Kim & DeVaney, 2001).
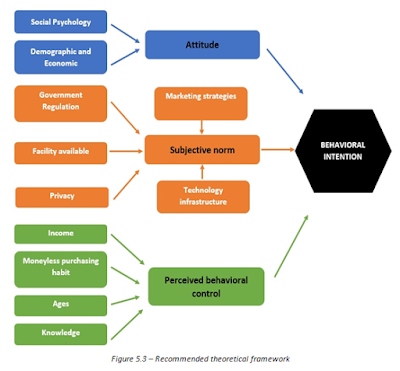
The development of credit card nowadays in Vietnam, especially in Ho Chi Minh City, is one of the top concerns of both consumers and providers. Based on the platform of Theory of Planned Behavior, with research topic: “Major factors that affect the intended decision to use credit card of people in Ho Chi Minh City.”, we propose a recommend model (Figure 5.3) to understand and study clearly about that.
Theoretical framework
Attitude : According to the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) (Ajzen, 1991), attitude is the first determinant of behavioral intention. It is the degree to which the person has a favorable or unfavorable evaluation of the behavior in question. Thus, consumer’s attitude toward credit can be distinguished into those subs – factors:
Social Psychology : Consumers may like to use credit card but because of social or situational pressure, consumers may decline use credit card (Ajzen, 1996). This sub – factor demonstrate that attitude might not necessarily predict intentional behavior. People normally vulnerable to environment and other factors affect directly or indirectly to human mentality, after that it will produce negative attitudes. Applying to this research, social psychology points out another framework in consumer’s attitude toward to credit card in HCMC.
Demographic and Economic
Consumers with different demographic and economic characteristics might develop different attitudes toward credit use (Bird, Hagstrom, and Wild, 1997; Danes and Hira, 1990; Modigliani, 1986; Zhu and Meeks 1994). Obviously, different consumer has different needs. Thus, their attitude different with each other whether or not negative or positive. There are some mini – sub – factors:
a. Ages : Younger people had more favorable attitudes toward credit card use than older people (Awh and Waters, 1974; Modigliani, 1986).According to this mini – sub – factor, instead of a simple preference for borrowing, those who are in early stages of their career might have more favorable attitude toward borrowing because they expect to have more future resources to pay off their debts.
b. Incomes : Upper - income consumers held more favorable attitudes toward credit card than did lower – income consumers (Mathews and Slocum, 1972; Slocum and Mathews, 1970). In short, those who have upper – income are less likely to be credit constrained and have more ability to pay off their debts than lower – income consumers.
c. Family Status : Children were positively related to the probability of having negative attitude toward installment debt (Yeih, 1996). Children usually think and act like their parent, thus it also effected to children attitude even though they don’t even understand about it.
Subjective Norms | Credit Card and HCMC Young People
According to the Theory of planned behavior (Ajzen, 1991), “The subjective norms referred to be the perceived social pressure to perform or not to perform the behavior.” and to be more specific, according to Bhattacherjee (2000) in Jogiyanto (2007:70), the subjective norms contains of two forms: interpersonal and external influences which influence others. Interpersonal influence is the influence comes from family, friends, colleges or experience individual who has potentially to become adopter. On the other hand, external influences come from the external sources: media, reports, experts or regulations of the government, etc. To the extent of the credit card usage, the two influence factors will help us to figure out (1) How far people which considered important and support from the others on the credit cards usage, (2) How far the information from the external factors can support people to use the credit cards. But in this dissertation, we would like to focus on the external factors in order to figure out the significant factors which can support the use of credit cards in Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam:
Government Regulations | Credit Card and HCMC Young People
Recent decades have been witnessed the fast growing in the number of cards issued in the market in Viet Nam (57.1 million cards in 2013, State Bank of Viet Nam), therefore, credit card market is not so new in Viet Nam and this is a fiercely competitive market because many banks can aware of the important of the ever growing of this service. In order to have a proficient market, the Government has to map out a certain integration plan and specific legal documents (transaction regulations, electronic payment, electronic signature…) in order to define the rights and obligations of parties (Armstrong and Craven, 1993; Heck, 1987). On the other hand, the government has to focus on the policies as well as regulations of protecting people when they access the cards services and the constrains between parties if the faults happen due to intentional or unintentional which cause risks for people using cards (White, 1998).
Technology Infrastructure and Facility Available
a. Technology Infrastructure : One of the critical factors that determine the success of the credit card business is the technology infrastructure in general and the individual credit card provider in specific (Amstrong and Craven, 1993). The selection of a customer to open or use a credit card in transaction of any bank is strongly depend on the technology that bank provided in order to satisfy their customers (Hayhoc and Associates, 2000). The improvements of the technology made a great impact on the business operating of banks.
b. Facility Available : Ho Chi Minh City is the largest city in Viet Nam with many retailing points, restaurants, supermarkets and shopping malls, therefore, the distribution of the point of sale (POS) for customer to make transactions with their credit cards is an important factor which can affect the behavior of customer directly. As we take ATM system as an example, according to Prager (2001), the costs to install an ATM is high but if any bank has the ability of bringing the availability to the customer (amount of machines, location, coverage), they will take the advantage of the market. We can figure out the important of the availability of the credit cards point of sale if the card providers want to grow further.
As traced back to the end of 2013, there were about 122.000 POS available for the customers in over the country and 26.000 POS in Ho Chi Minh City, Vice President of State Bank – Ho Chi Minh City branch (2013).
Marketing Strategies of Card providers.
Marketing strategies of the cards providers is an important factor to bring the services to people and improve their brand awareness. According to Siti Rahayu Hussin, Salina Kassim and Nuraien JaMal (2013), once the credit card providers can identify the credit card user’s characteristic and understand their usage behavior, they can be more successful . In addition, the customers will tend to have a self-conscious of belief that their card providers exist everywhere and they will feel more comfortable to use the cards.
Moreover, the cooperation between card providers and enterprises can bring the profit not only for both sides but also the customers due to the efficient advertising within the enterprises. Through that, customers can step by step improve the habit foundation of credit card usage with the help of utilities that cards can bring like fast transaction, convenient and safe.
Privacy | Credit Card and HCMC Young People
There are, of course, many different aspects of privacy, according to Byford (1998) , he focused on two different theoretical aspects of privacy, a social relationships view and a property view: “In the social relationships view, privacy is like a component to make the social relationships balance. Privacy is not much about the right to be alone, but as defined in American jurisprudence, as it is an important mechanism in social processes. In the property view, individuals see privacy as the extent to which they control their own information in all types of cyberspace exchanges. The property view manifests itself in willing exchanges of personal information in exchange for valued services such as free e-mail or special discounts from merchants.” Joey F. George (2004). Privacy is a part of important factors in which customers care much, because their money will be vulnerable if the transaction network is breakable and today’s technological crime is very dangerous.
Perceived Behavioral Control
According to the Theory of planned behavior (Ajzen, 1991), perceived behavioral control (PBC) refer to people's perception of the ease or difficult of performing the behavior of interest; it varies across situations and actions. Perceived behavioral control also depends on the resources and opportunities available to a person to achieve the behavior. Applying to the context of this research, this factor can be described through how a person can estimate their own capacity to use credit card by some sub-factors:
An individual or a family which has a great income should be more eager to use credit card (Kindsey, 1981). Obviously, income could have significant affect in decision to use credit card; one person would consider saving before spending money if he does not have a good income, especially with those who see credit card as a spending-temptation.
Moneyless purchasing habit
With the development of Vietnam economy, this new payment habit is considerable (Dr. Lê Thế Giới and Master Lê Văn Huy, 2006). Such kind of payment will bring the ease, convenience to the customer. They can buy things without carrying money along with them, especially expensive products. When they are at home doing online shopping, credit card is also the best and only choice for completing the purchasing process.
Ages
Old people seem not to take risk and use credit card (Barker and Sekerkaya, 1993). Especially, Vietnamese old people are quite interested in new technology but are not eager to use them. Credit card is a kind of borrowing money to spend and pay it back later with interest rate which is not in favor of old people. They do not want to take the interest risk.
Knowledge
The relationship between knowledge of credit card and the intention to use it is mentioned by many researches of Danes and Hira (1990), Barker and Sekerkaya (1992), Canner and Luckett (1992). With good knowledge and information about this kind of hi-tech product, customers will have more confidence to use them more frequently. With the rising rate of credit card frauds, this seems to be a significant factors in considering to use credit card as a mean of paying.
- Thesis Structure
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Theoretical Framework & Literature review
- Methodology
- Data findings
- Discussion
- Conclusion
- References
- Appendices
Research Design | Participants
The intended participants in our research will be the people who are under forty years old, live and work in Ho Chi Minh City and we intend to ask them to spend four minutes to complete our survey. The office workers are the first target of us because they account for almost half of jobs in Ho Chi Minh City, have more chance to approach the credit card services as well as many of them may need credit cards to do business. There may be students in Universities and they are the second important target for our survey too.
We would like to use the formula below to calculate the minimum sample size required and the adjusted minimum sample size needed:
Where:
• n is the minimum sample size.
• n’ is the adjusted minimum sample size needed.
• p% is the percentage belonging to the specified category.
• q% is the percentage not belonging to the specified category.
• z is the corresponding to the level of confidence required.
• e% is the margin of error required.
• N is the total population of Ho Chi Minh City.
The scales of the attitude, the subjective norms as well as the perceived behavioral control will be incorporated in the questionnaire. We will do the pilot test with our classmates and relatives who are office workers then calculate the adjusted minimum sample size of our research. All the questions in the questionnaire will be consulted by as many as our friends and lecturers as possible in order to get an appropriate questionnaire. We will have two versions of questionnaire, one will be in English and the other is in Vietnamese. After gathering and processing the data, we will use IBM SPSS statistics to analyze quantitatively.
Finally, the processed data will be used to identify the relationships between the attitude, the subjective norms and the perceived behavioral control to the intention of credit card usage of young people while applying and comparing with the previous published researches.
Searches related to credit card
apply for credit card
credit card bad credit
credit card for no credit
visa credit card
capital one
american express
chase credit card
discover
Credit Card and HCMC Young People Research Methodolory
Bạn đang xem một trong các bài viết tại Chuyên Mục credit-card. Và đây là địa chỉ link bài viết http://www.c10mt.com/2015/02/credit-card-and-hcmc-young-people-c10mt.html . Tâm Gà xin cảm ơn bạn đã theo dõi bài viết này. Đừng quên nhấn LIKE và Chia Sẻ để ủng hộ Tâm Gà nếu bài viết có ích !